A review of Inio Asano’s Nijigahara Holograph. Translated by Matt Thorn.
“If only the last dozen years were just a dream my younger self was having, how wonderful that would be.”
* * *
When the publicist for Inio Asano’s Nijigahara Holograph suggests that the work has “Lynchian” qualities, he probably means to evoke David Foster Wallace’s definition of the word:
“An academic definition of Lynchian might be that the term ‘refers to a particular kind of irony where the very macabre and the very mundane combine in such a way as to reveal the former’s perpetual containment within the latter.’ But like postmodern or pornographic, Lynchian is….ultimately definable only ostensibly— i.e. we know it when we see it.”
There is some of this in Asano’s manga but it never reaches that level of absurdity and distortion which we associate with the films of David Lynch. Far closer is the waking nightmare of a film like Mullholland Drive where the character played by Naomi Watts fantasizes about success and discovers her own dead body even as she festers and decays in a dark apartment.
The clues to the dream state in Nijigahara Holograph are the butterflies which flit around the panels of the manga, an evocation of Zhuangzi’s butterfly:
“Once upon a time, I, Chuang Chou, dreamt I was a butterfly, fluttering hither and thither, a veritable butterfly, enjoying itself to the full of its bent, and not knowing it was Chuang Chou. Suddenly I awoke, and came to myself, the veritable Chuang Chou. Now I do not know whether it was then I dreamt I was a butterfly, or whether I am now a butterfly dreaming I am a man. Between me and the butterfly there must be a difference. This is an instance of transformation.”
The manga begins with a collage of past events; a god’s eye view of humanity which will be inexplicable to the reader until several chapters in. It seems for all intents and purposes to be the day dream of one of the protagonists, a grown-up Amahiko, who stares fixedly into the distance and down into the open mouthed burbling of his dying, cancerous father. Moments later, he is seen talking about his waking dreams to a complete stranger:
“These days…I have dreams. It makes me wonder if what I’m seeing now isn’t really just a dream.”
The rest of this short prologue are disconnected vignettes of characters as yet unknown, sometimes barely perceived: a soon to be familiar man eating dinner in front of his television; a couple having sex (or is it rape); a set of notebooks; and a half-seen girl about to divulge her past to a disembodied psychiatrist-interrogator (or so it seems).
A hundred pages on and a teacher (Kyoko Sakaki) is waking from a dream; lying on her futon, staring motionlessly at the ceiling of her room.
“Recently I have had dreams. Dreams of my days as a teacher. I recall the happy memories and the painful memories.”
The chapters which have preceded this moments have concerned her past students and just those memories. The page before this shows a student diving into a swimming pool as the same teacher cheers him on—a lucid moment before waking; a past recalled imperfectly. As Novalis once said:
“We are near awakening when we dream that we dream.”
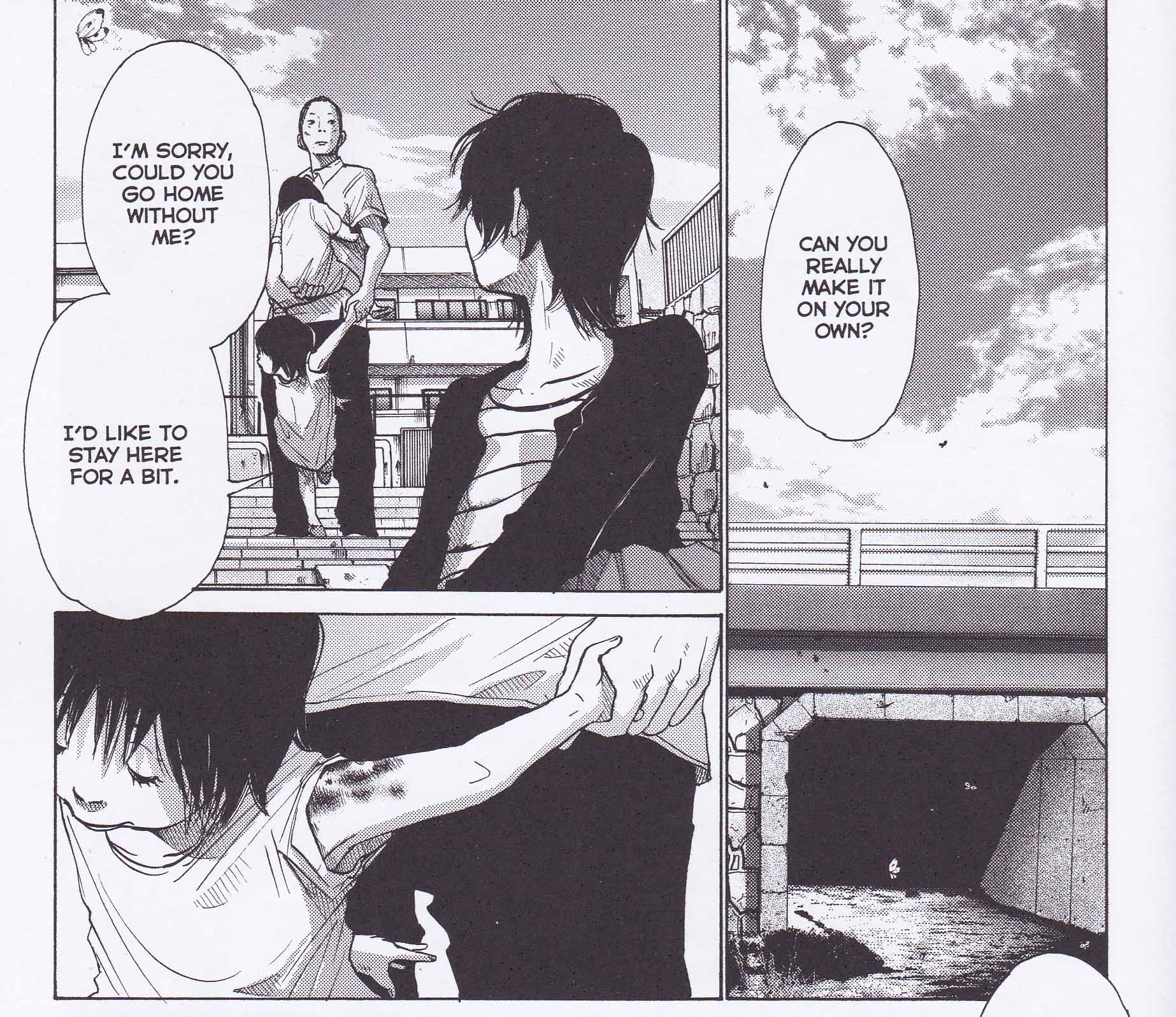
Kyoko Sakaki is about to awake to the traumas of her past. The question is whether she will disappear into them.
“I felt I could swim on forever. But I didn’t even know how to kick my legs or breathe properly.”
This is the essence of Asano’s dream narrative: a foreshadowing of events; a retelling of times past; a sequence of events which moves, without warning, between the past and the future—the induction of a hypnopompic state in the minds of his readers where we can barely distinguish between dream and reality.
Much of this comic will only make sense on rereading. Discrete scenes within the author’s framework only gain resonance when the manga is taken as a whole—an experience not uncommon to prose works but quite atypical of the manga industry where ease of reading is prized over much else.
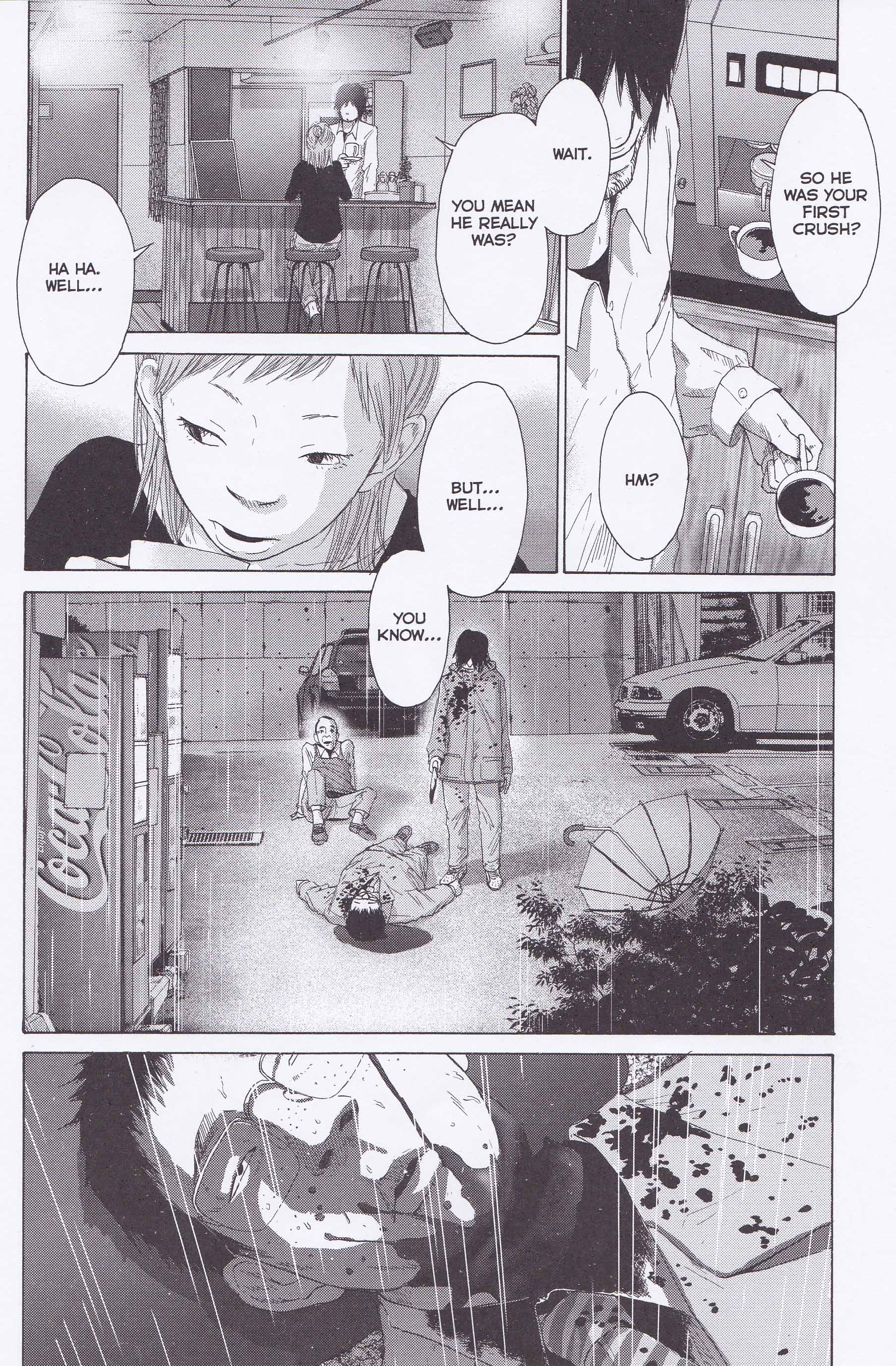
Consider the moment when Kohta meets up with Maki at the latter’s café workplace. They are old schoolmates and Kohta is Maki’s childhood crush. They met the day before after a space of eleven years and have had impulsive but congenial sex. Their meeting in the cafe is intercut with moments from Kohta’s murder of his grocery store employer (a former teacher). His threat of violence to a co-worker (who he has known since childhood) is intercut with his cold, unfeeling embrace of Maki. She agrees to meet with him at the Nijigahara embankment, a place only shown but unnamed up to this point—the monster’s refuge of children’s legend; the place of sacrifice to defer the end of the world; the nexus of all the vicious activities of that school and small community. The entrance to the embankment is an uncovered drainage hole, large enough to fit a child—both Kohta and his friend Kimura Arie are thrown into it earlier in the manga. The exit from this cave is the gaping underbelly of a bridge which yawns open like Grendel’s lair.
As it happens, Maki was involved in the attempted murder of Arie back in her school days, the latter’s body dumped into the same embankment. She reveals this sometime later in a drunken state to an admirer (her employer, Makoto). This short episode of no more than seven relatively silent pages is a repository of all the tension Asano has presented up to this point—the unexplained murders, the sought for vengeance, the desperate love, and sexual deviation.
The bestiality is everywhere but fragmented and barely broached in buried panels: the elicit love of a father for his pre-pubescent daughter (Arie)…
…the marks of abuse on an otherwise happy child…
…a faceless mother (stepmother as revealed later in the book) telling her son (Amahiko) to just die…
… the corporal punishment meted out by one of the teachers (the future grocery store owner)…
…and a senseless act of sororicide…
This last incident where Narumi is murdered off stage by her brother, Makoto, is both strange and painful in its elliptical denouement. Narumi might be the only character in this tale without a trace of malice and her death is an extinguishing of hope.
In fact, most of these acts of savagery are silently inflicted off panel save for an instance of rape.
This latter incident recalling—by means of an upturned umbrella—the previously described murder of Kohta’s employer.
The manga posits a world of existential and moral nihilism. Only the languid pacing and quiet narration prevents these relentless moments of brutality from overwhelming the reader. They seem almost matter of fact—a mother threatening her children with murder becomes no more than a creeping disease, like a father’s erection at the sight of the back of his daughter’s head. Not for these is the distress and despair of common humanity when confronted with “original sin”—like the media circus surrounding the murder of James Bulger for instance.
The appeal to Zhuangzi over the course of the manga suggest a deeper, more metaphysical nihilism if traced to our modern world—the exaltation in meaninglessness. The “monster” of Asano’s tale claims to have lost “something” on the fields of the Nijigahara embankment—perhaps it his conception of any sense of metaphysical values or consequences. As Nietzsche states in On the Genealogy of Morals:
“Nothing is true. Everything is permitted.” . . . Well now, that was spiritual freedom. With that the very belief in truth was cancelled. . . Has a European, a Christian free spirit ever wandered by mistake into this proposition and its labyrinthine consequences? Has he come to know the Minotaur of this cavern from his own experience?” [emphasis mine]
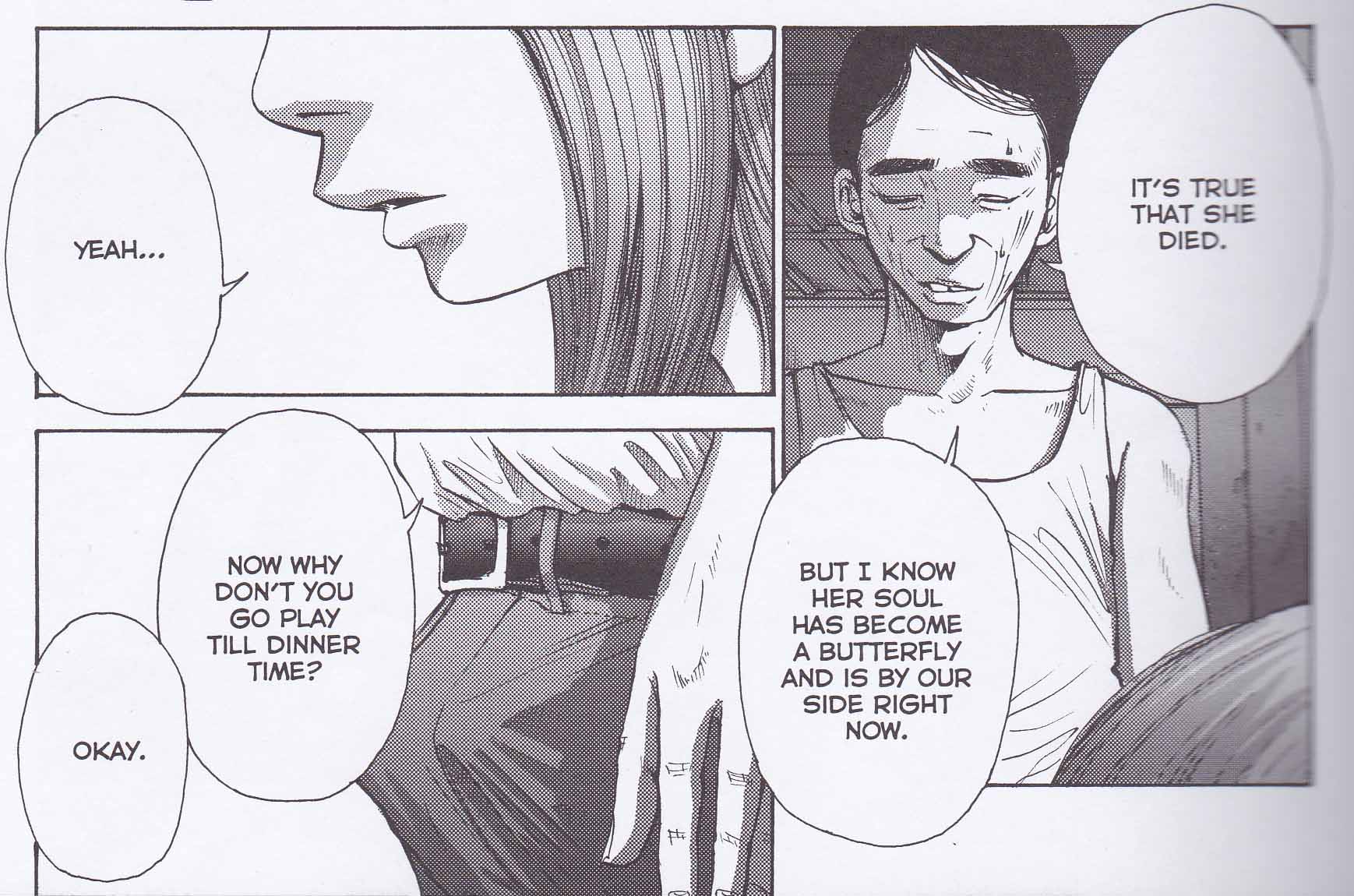
One proffered explanation for this nihilism (within the context of the manga) is that they are the product of Arie’s consumptive dreams. She has lain in a coma since being pushed into a hole in the Nijigahara embankment by her classmates. On visiting her incidentally in the hospital some ten years after her incident, one of her classmates wonders “what she’s been dreaming about all this time.”
Prior to her rape and attempted murder (these two events being only tangentially related), Arie had been telling and recording a “fantastic story of a world apart from this world”—a nocturnal land where a beautiful girl foretells a terrible future to seven villagers. Fearful of her, the villagers “cut off her head and [offer] her to the monster. ”It so happens, there are seven heads looking down into the hole where she has been cast right at the start of the manga.
On a final trip with her family to that embankment, Sakaki explains that the Nijigahara embankment was named for a legend about “Kudan”, a “cow with a human face” which is known to predict plagues and afflictions for a few days before dying.
“According to legend, whenever a Kudan was sent down the river, twin Kudans would be found at this spot. So “The Plain of Two Children” was its proper name. Someone later changed it to “The Plain of Rainbow.”
As must be obvious, Arie is the “Kudan” of Asano’s narrative. Or at least one of them, for she has a twin. And as Lafcadio Hearn explains in Glimpses of Unfamiliar Japan:
“…the Kudan always tells the truth.”
It is never made explicitly clear who the original Kudan of the narrative is—perhaps she is hidden in plain sight (see below) under an innocuous name like the illusory embankment of the manga’s title.
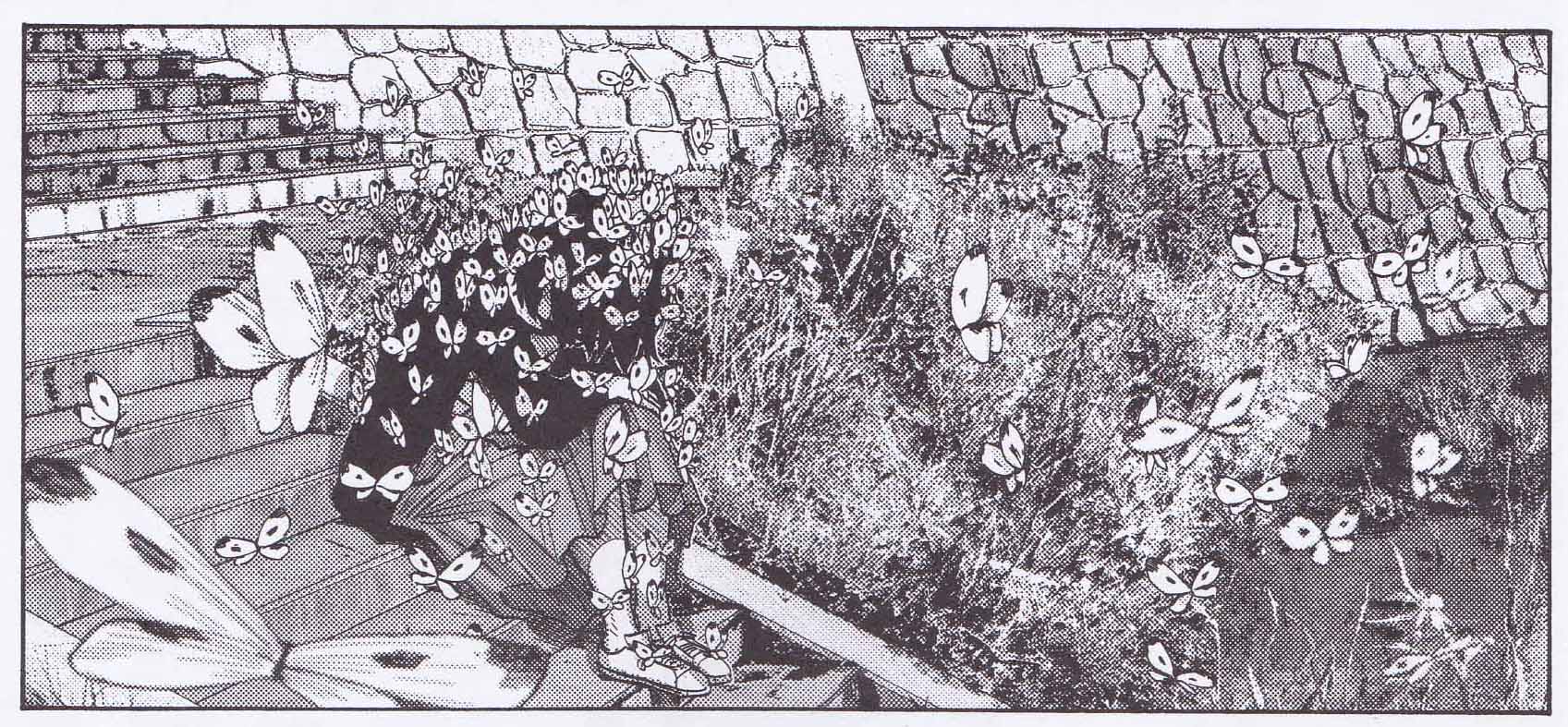
In her review of Nijigahara Holograph, Sarah Horrocks submits that it is this suppression of truth which explains all the anguish which follows. Sakaki’s dissolution into a myriad butterflies (see first image above) at the steps of the embankment suggests an inevitable (and symmetrical) recurrence of abandonment and death. The twins, Amahiko and Arie, are “abandoned” by the death of their mother, just as Sakiko’s twin children are abandoned by her grief and torment.
[Spoilers Ahead]
Finding readerly joy in Asano’s manga is not especially difficult, but it is predicated to a certain extent on heavy reconstruction. More than most comics, Nijihgahara Holograph is a web of half-hidden, splintered relationships which need to be pieced together like a jigsaw. The tangled associations of the various characters seem like a kind of inbreeding of cruelty and conception. There is, for instance, the affable pedophile, Makoto, who befriends Arie, encourages her stories of monsters, then rapes her before being stopped by her teacher (Miss Sakaki) who is then assaulted with a cinder block for her pains. Miss Sakaki is seen from the start of the manga with an unexplained patch over her eye and she is the same person who nurses feelings of violence against her own children.
Makoto (the violent pedophile) also happens to be the owner of the café which Maki works at eleven years later, the same café which Sakaki walks into a decade after her initial attack. It is only in retrospect that we recognize a silent panel—with Sakaki shown with her gaze cast downwards—during that fateful meeting as one denoting recognition. On a first reading, the panel in question is entirely unremarkable.
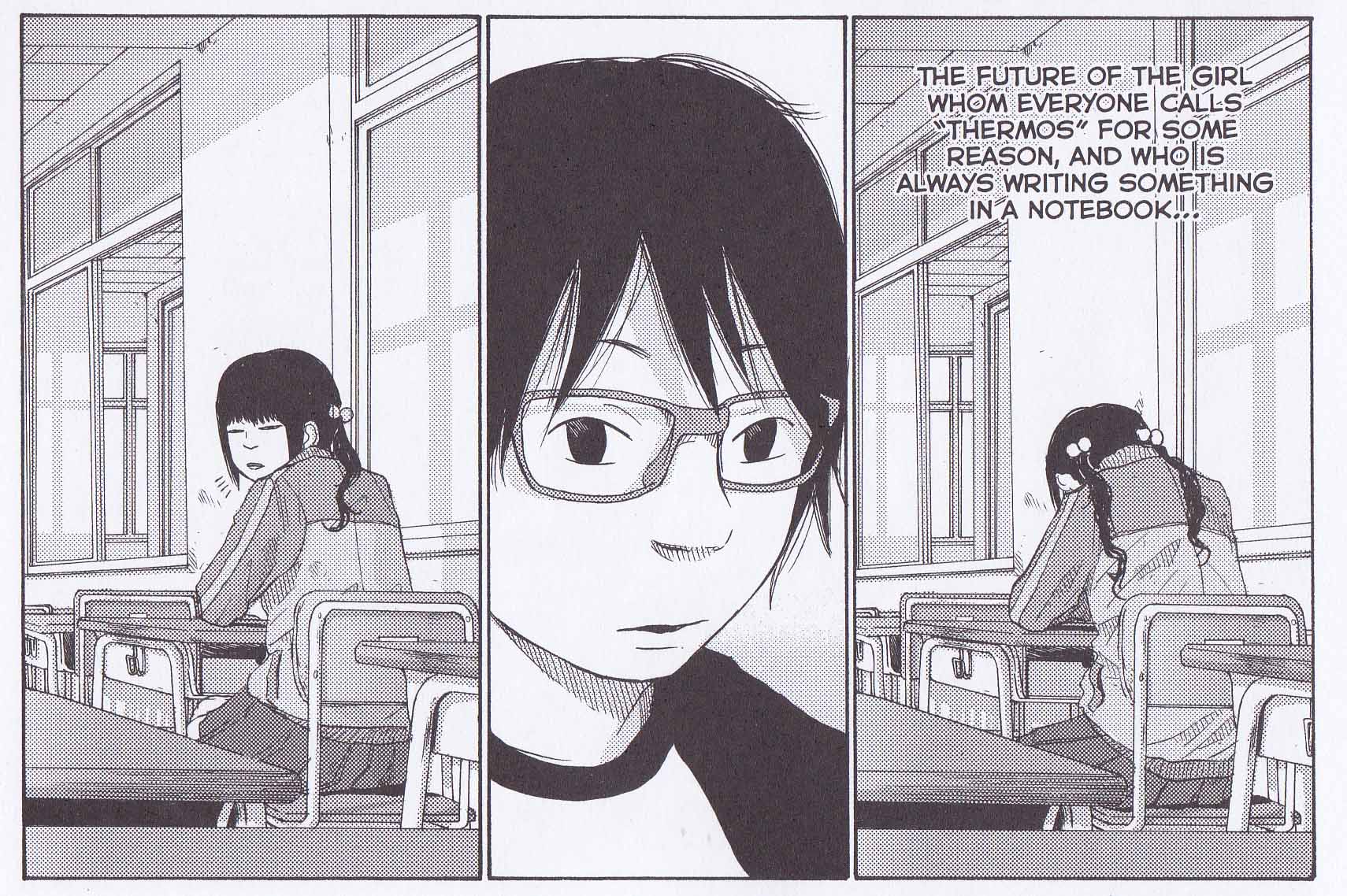
It only through these short hints and interjections that we realize that Makoto is a psychopath—the “monster” of the play. It is never entirely clear if Arie’s Cassandra-like foretellings are the work of her own imagination or a translation of Makoto’s communications to her. At one point early in the manga, Makoto’s sister, Narumi, is observed in class by Amahiko (the framing character of the manga and Arie’s twin) and noted to be “always writing something in a notebook.” Do these notebooks foretell a similar fate and is Narumi the original solitary Kudan of our tale?
The fairy tale of the beautiful girl and the seven villagers is only ever revealed in full by Makoto himself. This uncertainty is brought to the fore when we find out that Makoto has burnt down his parent’s house and (possibly) killed his sister (Narumi) for having discovered his murderous diaries. This is but one instance of Asano’s careful seeding of narrative and memory; not so much an exercise in mysticism but a fastidiously planned look into the suppurating secrets of a backwater town.
Let us return for a moment to Zhuangzi’s butterfly. In an article at Philosophy Now, Raymond Tallis explains the “radical uncertainty” presented in that Daoist text:
“Wittgenstein…pointed out that
‘The argument ‘I may be dreaming’ is senseless for this reason: if I am dreaming, this remark is being dreamed as well – and it is also being dreamed that these words have any meaning.’
Whether or not this is true, it is certainly the case that I must doubt that there is any audience for the words. Dreams are by definition solitary: they permit only the illusion of ‘we’. As Heraclitus said, “Only the waking share a common cosmos; each sleeps alone.” If there is no way out of the notion that the world is entirely my dream, there cannot be any way into it either, if only because there is an implicit ‘we’ in all language use, and even more so in conversation. I cannot truly share a sincere suspicion that I am at present dreaming…It reminds us that when we engage in philosophical inquiries fueled by radical doubt, we often overlook the very context that is necessary for the inquiry to take place, which has to be untouched by doubt. ” [emphasis mine]
There is no place (or need) for such contextual certainties in the encapsulated world of Asano’s manga which is driven entirely by fantasy. But there is everywhere considerable doubt as to the shared nature of Asano’s narrative of dreams—where do one character’s dreams end and another character’s nightmares begin? The closing passages of the manga both explicate and gently confuse the narrative coherency of everything that has preceded it.
The burst of disjointed imagery which opens the manga is as much a reflection of somnolent reverie as it is a statement of authorial intent; a blurring of reality and wish fulfillment; where past, present and future meet in a deliberate and calculated melding of form and content. The work as whole is a marvel of narrative needlework and one of the best comics to have been translated in recent years.
* * *
Further Reading
(1) Sarah Horrocks on Nijigahara Holograph (Parts 1 and 2)
“Violence is an important theme in Nijigahara, because one of the core aspects of the book is the constant repression by the community of prophecy, and the violent feeding of the monster who lives beneath that said community, in the tunnel at the Nijigahara embankment.”
“Life in Nijigahara Holograph is depicted through the management of trauma and memory. Adults become adults by what precious things they are stripped of as children, and how well they function as adults is down to just how well they can deny those memories….But in actuality, no one in Nijigahara forgets.”
(2) Matt Thorn on Inio Asano’s gender identity. No doubt someone out there has already linked Asano’s wish “that he could have a sex change” to the stories of the various twins in Nijigahara Holograph.













This was a great discussion of the book, which as you note demands a second reading.
Your review brings to mind some themes I’d missed, such as the relationship between solipsism and evil, and reminded me of aspects I’m still sussing out. For example, the reveal of the twins seemed almost pat, but I’m pretty sure there’s more behind it than the demands of narrative. Hmm.
Hmm, it is a bit pat but as a reader you’re sort of primed to accept it from page one since there’s the picture of the two babies right at the start. So it’s not a real surprise/big reveal. But you have to wonder if there’s more to it beyond the synchronicity in the plot (and the mental sympathy) – one twin falls off a building while the other gets pushed into a hole; one falls into a coma as the other awakens. Or are they both in a coma since Amahiko is only shown to wake up towards the end of the book? It’s obviously tied into the ancient Chinese-Japanese legends of twins being reborn lovers. But anything else?
Haven’t read the thing, but twins in comics always seem to me to highlight/work with the fact that comics are built around repetition of images; so two people who look alike in the same panel inevitably emphasize that you’ve got two images in two different panels of the “same” person.
FWIW.
I think there might be a bit of that working in Nijigahara Holograph – the main difference being that the siblings here are fraternal/dizygotic twins. So while they might not look alike, I think we’re meant to see them as the “same.”
There’s this whole other strange thing going on with their step parents as well.
676 Apparitions de Killoffer (by Killoffer) adresses multiple selves in comics with insane genius. The panel-less structure of the comic inevitably leads to the main character’s other selves to multiply in the same picture as him, until it becomes absolutely uncontrollable.
A great comic exploration of confusion and ordinary madness, and definitely on my “Top 50 comics that ought to be available in English” list.
“…it never reaches that level of absurdity and distortion which we associate with the films of David Lynch. Far closer is the waking nightmare of a film like Mullholland Drive…”
Excellent review. Just wanted to point out that ‘Mulholland Dr.’ actually IS a David Lynch film.
Pingback: Inio Asano, Nijigahara Holograph | John Pistelli