The powers that be are going to be doing some work on the site this evening. It shouldn’t be too disruptive, but comments may be disabled for a little bit, and you may notice other oddities. Everything should be back in place by early tomorrow. Sorry for the inconvenience, and thank you for your patience.
Three not-so-radical ideas for marketing manga to grown-ups
One of the things that struck me when reading Erica and Brigid’s contributions to the roundtable was that each proposed solutions that made sense for a particular audience. In Erica’s case, that audience is comprised of adult manga fans who have a passionate engagement with the medium, a knowledge of its history, and an active interest in the Japanese publishing scene, while in Brigid’s case, that audience is comprised of adults who are receptive to the idea of reading a graphic novel, but don’t know much about manga. As publishers like Vertical, Inc. and Drawn & Quarterly have demonstrated, these two groups’ reading interests do overlap; Buddha, Ode to Kirihito, and A Drifting Life are three examples of manga that appealed to a wide range of readers, from folks interested in good stories to folks interested in reading works by seminal Japanese artists. It’s this piece of the Venn Diagram that I’d like to address, in the form of three simple suggestions for marketing books to both audiences.
1. License manga that appeals to older female readers.
There’s almost no English-language manga about women over the age of 22 (at 28, the heroine of Tramps Like Us is positively geriatric), and little to no josei that features genuinely strong, independent female characters. (It’s telling that two of the best josei titles to be licensed for the US market, Bunny Drop and The Antique Bakery, feature male protagonists.) That’s where an artist such as Murasaki Yamada comes in; her work has things to offer the hardcore manga fan and casual reader alike, from her pedigree (she cut her teeth writing stories for COM and Garo), to her elegant, naturalistic style and feminist outlook. Which brings me to my next point…
2. Tell a good story about the book.
In their responses to Brigid’s post, Noah and Ryan Sands raise an important issue: meet-the-author events and book tours are an important marketing tool for generating interest among book-buyers and media outlets. Though a few publishers have brought Japanese artists to the US for signings, the process is complicated, in Noah’s words, “by language and distance.” In the absence of opportunities for authors and readers to interact face-to-face, publishers need to step up to the plate to tell readers what’s so special about the books they’re licensing. Drawn & Quarterly’s presentation of Black Blizzard is a good example of how to do just that. Consider the back jacket copy:
In 1956, at the age of twenty-one, Yoshihiro Tatsumi arrived as a major new talent in Japan’s burgeoning manga industry with the publication of his graphic novel Black Blizzard. With influences ranging from Osamu Tezuka to Alexander Dumas to Mickey Spillane, Tatsumi’s noir thriller displayed a cinematic, hard-boiled aesthetic, as well as a prodigious knack for inventive, fast-paced storytelling. Long out of print and never before published in English, Black Blizzard is a rare piece of Japanese cartooning history and an enduring work of high entertainment. Drawn & Quarterly Publications and series editor Adrian Tomine are proud to present this lost treasure from a modern master.
Without even opening the book to look at the pictures or read Tomine’s interview with Tatsumi, readers know immediately (a) who Tatsumi is (b) where the work fits into his development as an artist (c) who influenced him and (d) why Drawn & Quarterly’s edition is significant. Bonus points for connecting Black Blizzard with more familiar Western points of reference.
Now imagine doing that for an artist like Murasaki Yamada — not only are you appealing to manga enthusiasts who know about COM and Garo, but you’re also pitching your work to readers who enjoyed Persepolis and Fun Home by positioning Yamada as a similarly important female voice in comics (and one with an interesting biography as well — in addition to writing for two seminal manga magazines, she also ran for Japanese Parliament).
3. Get librarians in on the act.
As my colleague Eva Volin pointed out in an earlier discussion about manga marketing practices (this one focused on manga for younger readers), there are a number of compelling reasons to pursue the library market:
1) There are a lot of libraries.
2) We buy a lot of books.
3) We rarely return the books we buy.
4) If the book we buy turns regularly (circulates a lot), we buy extra and/or replacement copies.
5) If a category turns regularly we increase the amount of books we buy in that category.
6) By doing all this we create loyal readers who will often go in search of books at bookstores to buy and keep for themselves.
If you want librarians to buy your books and talk them up with patrons, however, you need to do more than just send out fliers and point to reviews; you need to meet with them face-to-face, explaining how your books fit into a well-rounded graphic novel collection, identifying the likely audience for your books, educating them about the creators, and giving them samplers or review copies. You also need to provide convenient ways for librarians to preview titles online — and you need to tell them about those online resources. The SigIKKI website is a great tool for librarians interested in building a graphic novel collection for adults, as it allows browsers to read entire volumes of manga for free and provides background on each of the featured artists, but if you’re not already a manga fan, how would you know about the site and what it has to offer?
Librarians can perform another valuable service for you as well: they can host events to raise awareness about your book, introduce readers to one of your authors, or engage them in a discussion of a broader theme. Done right, these kind of events can draw in long-time manga readers and newcomers alike, especially if you find a compelling hook for the material: a local mountaineering expert discussing the backstory to Summit of the Gods (and maybe sharing a few of his own pictures of Mt. Everest), an art historian tracing a particular manga-ka’s style back to nineteenth-century print-making traditions, a translator discussing the difficulty of adapting a script for English-speaking audiences, a film historian comparing scenes from a Masaki Kobayashi samurai film with sequences from Satsuma Gishiden.
__________
Update by Noah: The entire Komikusu roundtable is here.
Breaking out of the walled kingdom
There are two kinds of people in the world, my father used to say: People who divide all the people in the world into two types and people who don’t.
Comics readers tend to be the former: They look at the world as made of up of the initiated, people who read their particular type of comic (be it superheroes, shoujo manga, or introspective graphic novels) and those who are outside the walled kingdom.
There is some validity to that, because most comics genres, like most other genres, require a certain initiation. In the case of superheroes, you almost have to be born into it; one could spend a lifetime learning all the backstories, interrelationships, and alternate universes. Manga readers have to learn a code of visual cues such as sweatdrops and cultural clues such as honorifics and holidays, not to mention how to read right to left.
People who don’t normally read comics, on the other hand, don’t usually define themselves as “people who don’t read comics.” Most, in fact, will pick up a graphic novel if the subject matter interests them. They might not be able to enjoy something very genre-bound like Blackest Night or Battle Angel Alita, but they might read Fun Home, Mom’s Cancer, or The Photographer, because those books tap into more universal experiences and interests. A lot of people read those books not because they are comics (although the medium may make the story more compelling) but because they are books.
A lot of literary manga deals in topics that adult readers are interested in: Oishinbo (gourmet food), Ooku (historical drama and switched gender roles), Suppli (workplace comedy and romantic angst). These are good stories about things people care about, and you don’t have to understand the intricacies of samurai life or the Japanese school system to enjoy them.
But before you can read them, you have to find them.
Noah asked us a simple question: How do you market art manga to readers? The answer is equally simple: Don’t market it as manga. Market it as books.
Some specifics:
Don’t shelve it in the graphic novel section: The first step in reaching that broader audience is not to confine the manga to comics stores or even to the graphic-novel section of the bookstore. Ideally, booksellers should keep a couple of copies around, some in the graphic novel section and some elsewhere: Put Oishinbo near the food section, Barefoot Gen near the World War II books, Suppli by the chick-lit, Naoki Urasawa’s Pluto next to the science fiction. Scatter a few literary fiction titles (Tokyo Is My Garden, Red Snow) among the “staff picks” novels in the center tables.
Flip it: The purists hate this, but for older readers, reading “backwards” is a deal-breaker. Furthermore, it marks the comics as manga, and for those who aren’t famliar with the medium, that starts a whole chain of associations: porn, big eyes, teenage girls, boobs-n-battles. A lot of readers, wrongly, think of manga as a genre; manga for grownups must be marketed separately from the shonen and shoujo teen fare. Titles with broad crossover appeal should be made accessible to all readers, not just the cognoscenti. You can always publish an unflipped deluxe edition for the hardcore otaku.
Hire Chip Kidd to do the cover: Or someone like him. Make it arty and attractive. Do not fill it with slashing shonen battle action or an upskirt shot of a schoolgirl. (If those things appear in your manga, you probably shouldn’t be marketing it to adults anyway.) This should be a book you are proud to be seen reading on the subway, not something that would embarrass you if your boss saw it in your briefcase.
Send it out to “mainstream” reviewers: There are plenty of graphic novel-friendly reviewers at big newspapers and magazines, and they have a lot of pull. I first heard about Fun Home on NPR, and not because they were having “comics day” or anything; it just was a compelling story. As a journalist, I can tell you that a new and interesting topic is always welcome. A manga about a family with an autistic child? Bring it on! A manga about bluesman Robert Johnson teaming up with bank robber Clyde Barrow? Sign me up! These are topics that are interesting just by themselves, and the fact that someone in Japan has chosen to make a comic about them makes them even more interesting.
Also, you know what can really sell a title? Online previews at hip websites. There’s something inherently cool about manga, so the occasional free sample would most likely be welcome. Smith Magazine, for instance, hosted the webcomic AD: New Orleans After the Deluge, and Words Without Borders has a whole graphic lit section. These websites already cater to readers with a literary and artistic bent, so they are likely to be a receptive audience for art manga.
Go digital: You knew I was going to say that, right? Everyone is doing it! The Kindle, the iPad, and the plain ol’ internet are places your potential audience can discover your manga and instantly read it. Here’s the thing, though: Go ahead and put your manga into comiXology and Longbox and those other … things… but let them stand alone as well. Recently, Longbox developer Rantz Hoseley talked about the possibility of having a link directly from a story on, say, the NPR blog, to their digital edition of a comic. That’s a great convenience, but the occasional comics reader just wants to read the book, not sign up for some complicated digital storefront that they will never visit again.
Harness serendipity: All these factors boil down to the same thing: Make it easy for potential readers to stumble upon a book, and once you catch their interest, make it easy for readers to buy it. Go back to the dichotomy I started with: Serious comics readers know where to find comics and how to buy them, but it’s a system that is invisible to most people and forbidding to those who do know about it. Superhero fans may be willing to go out of their way to a special store and pre-order their comics sight unseen, but the rest of the world doesn’t operate that way. Even the graphic novel section of a chain bookstores is terra incognita to most customers. The key to expanding the comics market, for art manga or any other type of graphic novel, is to step outside the closed circle of the comics world and find the readers where they already are. After that, the books should sell themselves.
__________
The entire Komikusu roundtable is here.
The Solution to the Scanlation Solution
This article was originally posted on Okazu, as a discussion of scanlation in general, but this discussion is even more relevant to “arty,” more grown up comics, which will, by it’s nature, appeal to a smaller audience than anything mainstream. The smaller the potential audience, the smaller the potential market. Because it’s hard to get what they want to read, this audience created scanlation to serve their needs.
Here is a history of scanlation – and a suggestion for a solution that can be most effective for the titles least likely to reach their market with the current distribution models.
****
Scanlation – the widespread, illegal act of scanning in books/comics/manga, sometimes translating them into another language and distributing them for free through digital formats and technologies.
Scanlation is, everyone will agree, a big problem. The comics publishing industry is losing sales even as downloads of scans hits numbers that most comics publishers can only dream about. The comics/manga journalists agree, talking as they do to the publishers and creators – who feel particularly angry in regards to the wholesale refusal of their “fans” to respect their IP rights. And the pundits who discuss the quickly disappearing value of copyright and IP ownership agree.
Cartoonist Scott Adams recently blogged on this disappearing economic value of content as it becomes easier to search for – without necessarily being involved in a ‘scan’dal himself. (Adams allows free and fair use for all his work, and encourages fans to do mashups, parodies and original work based on his material.
So, if everyone agrees that scans are bad, why are they so rampant? How can we fix this pervasive problem?
In order to fix the problem, we have to step back and realize that scanlations are not the “problem” – they were the solution.
I’m speaking here as a fan of manga, comics from Japan. When I started to read manga there were – to be generous – very few titles licensed and translated.
The fans who loved manga saw the problem clearly – there was a lot of cool stuff being drawn in Japan and very little of it was translated into English. So, they formed groups called “circles” – passionate volunteers who pooled skills and resources into scanning in manga and translating them. This way, they could share the series they loved with other people who would never otherwise get a chance to read them. It was (and largely still is) a love for a title that leads a person to scan it – not a desire to harm, but a deep desire to share and expand the audience.
Scanlation was the solution to the problem. It wouldn’t hurt anyone – none of those books (or anime series) were ever going to make it over here, so no harm, no foul. At least one person had to buy the book (or VHS tape) in order to render and scan it, so there was at least one additional sale to “pay” for the work. No scanlation circle ever made a cent on their efforts. They gave their love away for free, so they could call it fair use. And they were very specific – if you paid for a version of their scans or subs, you were ripped off and you were committing a copyright violation.
Then the digital revolution really hit and suddenly more series than ever were being scanned and subbed. It isn’t hard to get a scanlation – all one needs is a browser and a search engine. What had formerly been distributed to dozens of people was now being distributed to thousands or tens of thousands worldwide. Hits on popular scanlation aggregation websites go into the millions, bringing at least one such site onto Google’s list of top-visited sites.
And, in the middle of this, distribution companies started to license more series than ever. But now it was even easier to scan than before – often a scanned raw version is available, so no original copy is bought. Scanlators can put out a whole volume in days in just about any language a group might want. And the more popular, the more ubiquitous the content becomes, its economic value drops ever closer to zero.
What we need now is not a solution to the problem, but a solution to the solution.
***
Scanlation affects three entities. The fans, for whom it is uniquely an excellent – and elegant – solution. The publishing companies, for whom it is a strongly negative factor in both incentive to license and in actual sales. And the creators, who are often clueless about the scale of the issue, feel helpless and angry if they are aware of it, and whose bottom line is the most damaged by it.
For the sake of meaningful discussion, I am going to ignore the existence of overtly criminal scanlators and subbers. These are people who illegally distribute books and series that are legally licensed and available in their country. They know they are committing a criminal act and do not care. Their audience is either naïve and unaware that these distributors are illegal – or they are aware and, like the scanlators, do not care. These people are engaging in IP theft and copyright violation with criminal intent. They are not relevant to this discussion, in which we are going to address the “problem” created not by the desire to steal – but by the desire to share.
I say that scanlation is a solution. The problem it solved was “things I want to read are not licensed for my country.” This was true in 1998 and now, in 2010, it is largely *still* true. I follow a genre called Yuri (lesbian-themed stories), which has had a Renaissance in Japan, but is almost completely unlicensed – and in many cases unlicensable, as the content is difficult, if not outright impossible to market in the western world.
I learned Japanese to be able to read these books but, for most of the audience, this is neither sensible nor viable. Scanlation of this genre is still driven by love of the genre and desire to share with other fans – this is the motivation of an “ethical” scanlation group.
Let’s take a look at a typical “ethical” scanlation circle as they exist now.
An “ethical” scanlation circle only scans series that are unavailable in their primary language. They strongly encourage their readers (what I refer to as “the audience”) to buy the book (to become “the market”) when it is licensed in that language. They do not charge for their efforts, do not have ads on their website, do not take monetary contributions to their efforts. Ethical scanlators may ask for donations, but are more likely to want resources (bandwidth, seeders, expertise, etc.,) than money. It’s a labor of love. These circles are often composed of people who do buy that original copy or two – and many of their senior members may also purchase the book in the original form to support the creator. Ethical groups pull their versions off the Internet – and ask their fans to stop sharing theirs, should they have them – as soon as news of an official license is announced for a work. And because ethical groups are trying to help, not harm, it’s a high probability that if creators asked them directly to stop scanning their work, they would.
I believe 80% of groups would stop, because as sad as it would make them feel, they really are only trying to help. That would leave 20% who voluntarily enter the real of “criminal” scanlators, in the sense that they know they are going against the creator’s wishes and violating their IP rights, but for whatever reasons, don’t care. Japanese and American manga publishers have just created an alliance to attack this 20% tip of the iceberg. I think this makes sense for them and wish them well at it. It is wholly within their rights and responsibilities to protect their IP. Interestingly, many of the ethical scanlators also dislike the aggregation sites precisely because these sites distribute material they have no right to distribute, i.e., work done by scanlation circles. Ironic as it is.
Despite the ethical scanlators’ best intentions, not all of their audience is as ethical as they are. Not everyone in their audience wishes to support the creators or the publishers. Many plead lack of funds as a sufficient reason to only download scans. Some fans have oddly selective memory and will recall a slight from years ago by a publisher who dropped the ball, and will use that as justification for never buying from that company – even if by doing so they would be supporting a creator whose work they love. For many of the audience scans are their only option, as no companies in their countries have made an attempt to license what they would like to read. For these people, scanlation continues to be fair use of the content.
Lastly, there is the issue of translation. One of the pervasive arguments against scanlations is that official translations are better in all ways. Unfortunately, this is very often not the case.
Publishers are bound by contracts, copyright, and requirements from the licensors, creators and market forces. A name may be commonly translated by the fandom in one way only to be altered by the licensor or creator to something that looks/sounds/feels utterly absurd to a western fan. I can remember reading a book in which the main character’s family name was Naitou, but for some reason, the creator wanted it spelled Knight-o…which just looks silly on the face of it. If a character’s name rides the edge of a possible copyright infringement, it must be changed, not because the publisher hates the fans, but because there is no comics publisher around that can afford ongoing lawsuits with major western media companies who guard their copyrights with an absurd, creativity-killing zeal. Publishers are at the mercy of hired translators and editors who they hope are accurate and skilled. And, lastly, publishers are bound by the need to *sell books.* This means that a publisher may make a decision to change something to make the book appeal to more than just the core audience – sometimes at the risk of offending the core audience. Scanlation groups are not bound by any of these issues and are free to translate names in a way that is a common usage among fans, or which makes the most sense.
Scanlation groups often do a tremendous amount of research, to explain puns and literary references, offer historical context, descriptions of military terms, define common honorifics and generally provide the reader with as authentic a reading experience as possible. Publishers, for any number of reasons, will often not do this. In one case I can think of, a licensed series that previously had detailed translation notes has now had them cut back to nearly nothing, so that many of the references simply go undecoded. It might be because of money or time, but many licensed series can’t provide that level of detail. Not every scanlation group does this, of course, nor does every publisher skimp, but I can easily call to mind several series in which the scanlation groups did a better job than the legit publisher and several groups who work is professional quality (in some cases because professionals work with them.)
And, finally, there is the issue of out-of-print material. I will admit that, up until a few years ago, I was providing a scanlation group with material from a magazine that is long out of print, never had collected volumes and was in danger of disappearing, forgotten. I have stopped, because of my shifting feelings about scanlations, but I do not regret having done what I did.
Some of the American comics scan sites distribute back issues – the infamous HTML Comics touted that as their raison d’etre. The owner of this site, which has now been shut down by the FBI, insisted that the companies left him alone because he only made old material available. It’s true that a die-hard fan can find any number of avenues to find and purchase Thor #142, but for a casual reader, it makes no sense to attend a show or hunt online for a single volume that you simply want to read once. That’s why libraries exist in the real world – and there are no pamphlet comics libraries available to the average person in Whatevertown, USA.
The sole problem, really, with scanlations is that they are illegal (and, perhaps, immoral.) The scanlation group is distributing something they do not have the right to distribute. In effect, if they could gain permission from the creator, scans would *still* be a very elegant and simple solution to the problem. Permission is very much the crux of the matter here. Musician David Byrne wrote about a creator’s right to grant permission on his blog, in which he says plainly, “It’s not just illegal because one is supposed to pay for such use and not paying is, well, theft — it’s also illegal because one has to ask permission, and that permission can be turned down.”
So, in the past, the problem was “things I want to read are not available” and the solution was “scanlations.”
Now, what is the current problem? Not scanlations, which are the solution to a previous problem.
I propose that the problem we are really dealing with is this:
1) Readers want what they want to read, in their language, for a reasonable price (or free), in a reasonable time frame, in a format that is not reliant on a single standard, format or hardware.
2) Creators want the right to make decisions about their work, grant access and distribution rights, give *permission* and make a fair wage from their work.
3) Publishers want to be able to sell materials that they have paid to license (or to create) and make enough money in doing so that they can pay their employees, themselves and have money to invest in new properties.
For readers, the problem hasn’t changed all that much. Readers’ expectations have changed, because at this point it seems absolutely absurd that I really can’t just get what I want to read in my language. Regional licensing? Why? Clearly it doesn’t help Czech readers to learn that a Korean version has been licensed, or English readers that France will get a release of a book they’d like to read too. The fact that DVDs are still region encoded when most DVD players are no longer limited by that seems more of a sad memory of some ancient gerrymandering of the planet than anything useful or intelligent. Where is our global economy?
For the creators, the problem hasn’t changed at all. Where once upon a time, the companies took your content, threw you aside, then wrung the content dry, now the fans do it too. Nice way to say “thanks” for all that hard work.
And for the publishers, the problem is seemingly endless and constantly shifting. How to determine what titles are most likely to actually sell, to license work people want, get it to them quickly and with high quality, and for free, then provide a way to sell books as well, without involving a distribution model that relies on some third-party company whose decision-making is schizophrenic at best and seems pretty heavy-handed all the time, or whose hardware requires a proprietary format.
The solution we need must address at least the first two of the above three issues. It’s already clear that publishing is changing, and if the role of publisher disappears into a world in which readers and creators interact directly and meaningfully then I, as a publisher, don’t mind all that much. But, I do think there is a place for publishers in the new solution, even though the concept of “publisher'” will change.
Now, all that has gone before is a discussion of “The Problem,” which was really just the solution to an earlier problem. It’s time to consider the “The Solution” to our new set of problems.
I had this discussion on Twitter and received an enormous amount of excellent feedback. Here are some (not by any means all) of the specs of the new Solution. None of these are my ideas, this is a synopsis of the collective mind.
But, before we move into the specifics, I want to be up front and address the obvious argument against what I am about to lay down – it all seems utterly unreasonable. Of course it is. It’s crazy thinking. Off the rails. This is not a solution that fixes a problem – what we need now is a solution that creates an entirely new vision. I believe that the heart of this new solution is in the core of the old one – the passion and love the fans have for comics and manga. I’ve seen both technology and process shifted by scan groups as a way to better serve their audiences. If we can harness that to begin with, we’ll have a strong start.
The solution needs to be platform- and technology-independent. Not hardware dependent, not company/distributor dependent. Manga Expert Jason Thompson posted recently about how badly the iPad serves manga with schoolmarmish standards of what is “appropriate.” Many articles exist about how Kindle and Nook at this point, are not good for graphic novels. There is more commentary about the increasing difficulty of distribution of printed comics and manga than any one person can really keep up with. We need something better, something that allows creators to make their own decisions about how their work is viewed and readers to make our own decisions about what content we choose to read.
There must be self-regulated community standards so that children can find comics that suit and so can adults, without having to be “protected” from porn by over-zealous hardware gods.
Creators should get payment for every download/view and also reasonable payment for every approved modification, parody or use of their material. For instance, if a creator approves a translation of their comic to Uigur, a small fee (one in proportion to the number of people on the system with that as their primary language) can be paid by a group, so they can then translate that work into their language. The download/view fees will then pay the creator royalties for their content. Comic artists will have control over what happens to their work, and will be paid for the use of it.
“Publishers” will be anyone who is not a creator, but modifies a work by translating, editing, retouching, relettering, etc, for an approved project. This will give passionate fans the ability to share their favorite works in a legitimate manner. Perhaps these “publishers” can get a percentage of the approved projects that are downloaded/viewed. For instance, if that Uigur scan group is composed of 5 people, every time the Uigur translation is read, the translator, editor, proofreader, letterer and retouch person might get a small percentage of the download/view fee. 95% of the fee would get to the creator who approved the work and each of the scanlators might get 1%. Tie scanlation circle ratings to the relative financial success of the work, and the ratings will indicate to a creator not only the skill a circle brings to the problem of translation, but also their marketing strength. Circles will have a direct motivation to make sure the creators make money on their work, or their own ratings will fall.
There needs to be a creator community and a reader community as part of this solution. Every scanlation group has a community and it’s this that keeps the group – and the love – alive. Fan work can/will be encouraged, but also managed. Some creators are already going this route on their own – taking their work online and developing their own methods to monetize it. This solution would provide a home for all creators, worldwide, to do the same, in a way that allows them to focus on their work, not on the technology of distribution.
Reader and system suggestions – and free previews of series that are not in the readers’ normal genres – will help stimulate reading.
And, for those of us who still love the feel, smell and look of books – print on demand capability, with reasonable price points. Like pamphlet comics? As long as the creator gives their approval, each chapter can be printed that way, or as a whole GN volume. The creators will have the opportunity to merchandise directly in the form of whatever products they want – T-shirts, postcards, or limited printed lithographs of a cover piece. It will be up to each creator to decide what they want to do and what form it would take.
Take the passion already put into scanlations, give it the power of community, suggestions and ratings, add the freedom of webcomics, a creator community in multiple languages and above all of this allow *permission* to be granted by the creator and fees to be paid for the use of the content.
I am not smart enough to do this, but I am convinced it can be done. It’s not in a company’s best interest to come up with the solution – companies have to pay bills, they have to protect the IP they have and the status quo of how they work. It’s not in our best interest to let the companies dictate the formats and hardware we use to read our manga.
I challenge all of you out there to create this new solution. And I challenge you to all work on this, not wait for someone else to build it. Scans were developed by fans to solve a problem. Don’t focus on the problem – or why this can’t work – focus on the solution and how it can – then let’s make it happen. Also, let’s lose the fannish binary of either/or. There can be *multiple* streams of distribution in this world. There’s no reason to think that this solution can’t exist parallel to seven other forms of distribution, including magazines and books.
For the creators who want control of our work and readers, who want freedom to enjoy that work in our own way this is an unparalleled opportunity. We can all create a new paradigm that will make readers, creators and publishers equal stakeholders in an industry and in the content we all love.
Erica Friedman is a content creator, a publisher and a reader.
___________
Update: The entire Komikusu roundtable can be read here.
Komikusu — Introduction
A couple weeks back Sean Collins wrote a post over on Robot 6 asking folks to propose comics arguments they’d like to hear more often. In comments, on that thread, Kate Dacey offered this response.
There’s a similar divide in the mangasphere [between art comics and more popular titles] as well: a lot of sites focus on mainstream shonen and shojo titles (the manga equivalent to tights and capes, I guess) while neglecting the quirkier stuff. To be sure, there are many sites that cover the full spectrum of titles, or focus on a niche, but the pressure to stay current with new releases and draw traffic discourages a lot of folks from waxing poetic about the stuff at the fringes. Looking at my own site stats, for example, a review of Black Bird or My Girlfriend’s A Geek will attract a much bigger readership than, say, The Times of Botchan.
Which brings me to the argument I’d like to see explored somewhere: how do we interest older readers in manga that’s written just for them? What kind of marketing support would, say, the VIZ Signature line need in order for some of those titles to crack the Bookscan Top 750 Graphic Novel list? Are there genres or artists we should be licensing for this readership, but aren’t?
That sounded like a great argument to have to me…so, with Kate’s help, I’ve organized a roundtable on HU to explore the issues Kate has raised. The critics who have agreed to participate are, in no particular order:
Kate Dacey of The Manga Critic.
Ryan Sands of Same Hat!
Brigid Alverson of lots of places, inlcuding Mangablog.
Erica Friedman of Okazu.
Shaenon Garrity who writes at tcj.com.
Deb Aoki of About.com.
Ed Chavez of Vertical.
Peggy Burns of Drawn & Quarterly also graciously granted permission for me to reprint a short email she sent me in regard to the roundtable, so that will be appearing in the mix as well.
The title of the roundtable was suggested by Ed Chavez:
I would possibly call it… “Komikusu” (Comics) is Japanese for manga
The reason I’d say that is in the seinen and the experimental manga world most manga is not called manga it is literally called comics. However for the longest time pubs and editors there have gone about presenting this category (particularly seinen which happens to be the most stable demographic in manga) as sequential art for the masses. Not just for kids or teens, men or women, but for anyone.
Erica Friedman will kick off the conversation tomorrow, and others will be posting throughout the week. Many thanks to Kate Dacey and Bill Randall for their suggestions and help in pulling this together. And of course thanks to all those who agreed to participate: I’m really looking forward to it!
________
Update: Erica’s post is now up.
DWYCK: Hergé and the Order of Things
We’ve had a fair amount of discussion about how to approach comics critically here at HU lately, and I figured I’d expand a little upon some of the points I’ve made previously regarding cartooning as a visual phenomenon.
From a modernist critical perspective, it seems clear that comics’ artistic achievement through their modern history — i.e. the last 200 years or so — is predominantly visual, and it seems equally uncontroversial to say that the visual aspect of cartooning has generally been given higher priority by cartoonists as well as fans. This has to do with comics’ history as a low culture mass medium produced primarily to entertain and the genre constrictions this has placed upon its development.
The absence of a sophisticated, independent tradition for the appreciation of comics as art — in the broad sense, not just visual — means that critics have to start somewhere else, and given comics’ focus on narrative and their appeal to students of culture, the point of departure has more often than not been literary.
Unsurprisingly, comics have fared badly. Rote humor and trite genre exercises permeated by cliché and unfortunate stereotyping just don’t hold up to critical scrutiny when compared to the achievements of literature of the kind written in just words, no matter how pretty it looks.
To an extent, this is healthy. For comics appreciation — and indeed comics — to evolve, the medium needs to be subjected to the same probing scrutiny under which other artistic media have developed. Comics should be given no condescending breaks. However, they also need to be recognized and valued for what they are, for their particular synthesis of word and image and its fascinating cultural permutations.
Paradoxically for such a visually effective and attractive medium, very little attention is paid by critics to their visual aesthetics, and what little theory we’ve had — from McCloud to Groensteen — has concentrated primarily on their means of making narrative meaning.
Although it would certainly do some good, more criticism from a traditional visual arts perspective wouldn’t be sufficient. It would probably take to comics’ weird mix of simplification and exaggeration only slightly more charitably than has traditional literary criticism (consider the place satirical and gag cartoonists occupy in the art historical canon for reference). What we need is a new way of looking — one that doesn’t start by separating “story” and “art.”
Unsurprisingly, some of the most promising steps in such a direction have been taken by cartoonists, who have always been aware, if often only intuitively, of the special nature of their craft. In his recent foreword to the first volume of his collected Village Voice strips, Explainers, Jules Feiffer writes:
“I thought [the drawings] were stylistically subordinate; words and pictures are what a comic strip is all about, so you can’t say what’s more important or less. They work together. I wanted the focus on the language, and on where I was taking the reader in six or eight panels through this deceptive, inverse logic that I was using. The drawing had to be minimalist. If I used angle shots and complicated artwork, it would deflect the reader. I didn’t want the drawings to be noticed at all. I worked hard making sure that they wouldn’t be noticed.”
This notion is echoed in Chris Ware’s oft-repeated notion of cartooning as a kind of drawing that you read rather than look at, and in the old truism that great cartooning is akin to signature — the cartoonist’s handwriting. Think the inseparable entity that is Schulz and Peanuts and it pops.
Although it doesn’t apply equally to all forms of cartooning, this is an essential insight, not the least in that it connects the art form at a fairly basic level to the origins of the written word in ideograms. But it simultaneously runs the risk of devaluating aspects of comics’ visual life, once again making image subordinate to writing and reducing comics to “texts.”
Let me propose an example. Hergé’s Tintin is one of the most influential comics of the European tradition. It has entertained generations of readers all over the world and pretty much established the blueprint of clear storytelling in long-form comics, much like Schulz did for self-contained comic strips.
And while it is one of the rare comics that has been enshrined in high culture, at least in French-speaking countries, it still provides a good example of how great comics art may suffer in the encounter with traditional high culture criticism. It is very easy to reduce the Tintin stories to fairly unremarkable genre romps leavened with wholesome humor and only occasionally packing a certain and never particularly sophisticated satirical bite, all the while being stirred by troubling — if significantly also troubled — ideology.
The enduring popularity and greatness of Tintin, however, runs deeper, and it is inextricably bound up in the cartooning, not merely as storytelling but as personal handwriting. Peanuts wears Schulz’ emotions on its sleeve and is therefore more immediately appreciable as a work of literature than Tintin, which encrypts those of Hergé in a consciously dispassionate representational vocabulary.
The ligne claire, as it has become known, eschews hatching, downplays contrast, eliminates cast shadows, and maintains a uniformity of line throughout, paying equal attention to every element depicted. In his mature work, Hergé took great care to describe everything accurately, giving the reader a sense of authenticity and place. He did this not through naturalism, but rather through a careful distillation process, rendering every phenomenon in a carefully calibrated visual vocabulary that presents a seemingly egalitarian, ostensibly objective view of the world.
Reflecting his Catholic upbringing and the boy scout ethos which had been so formative to him, his cartooning is about imposing order on the world. His art is a moral endeavor that traces its roots back to the Enlightenment. At the same time, however, it reflects the futility of this endeavor, suggesting more mercurial forces at play.
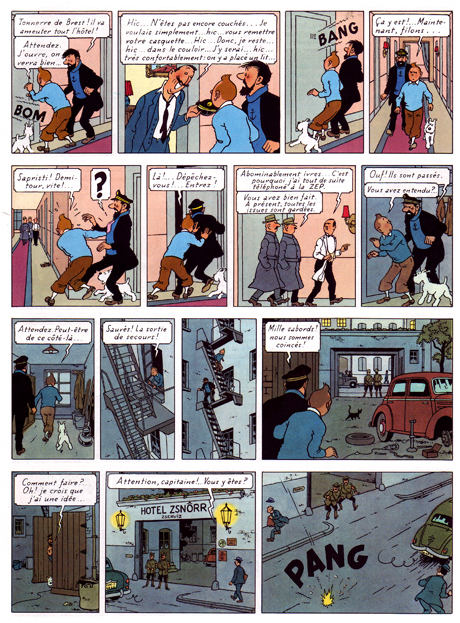
One of his most sophisticated works, The Calculus Affair (1954-56), articulates this tension beautifully. Page 50 is as fine example as any: the story is a fairly straightforward cold war cloak and dagger yarn, with the present sequence concerning Tintin, Haddock and Snowy’s escape from a police-guarded hotel in the Eastern Bloc country of Borduria.
The storytelling is characteristically clear and one might find sufficient an analysis of how the choice of viewpoint supports the action depicted, how the characters’ move from panel and how the space in which they move around is so clearly articulated, etc. But this would primarily be an analysis of how we read the sequence — what I’m interested in here is rather the vision it manifests.
As a comics maker, Hergé was acutely aware that he was speaking through fragments. Much of his art is concerned with this issue and the present book is among his most disciplined and intelligent treatments of this basic condition of comics. Framing clearly is the unsettling factor in his vision.
Most obviously, it occurs in his arrangement, both of the page — where the odd number of panels disrupts slightly its seemingly ordered construction — and in the composition of individual panels. He is an expert at this, keeping each panel interesting without cluttering it unduly: a cropped lamp and picture frame suggest a hotel room interior (panel 2), but also provide surface tension in an image of slight disorder. Tintin’s figure is disrupted by the outheld cap and line defining the wall paneling. Hergé’s is a controlled, subjectively ordering gaze.
The sequence is about movement and liberation by means of a metaphor of illumination. Dividing the page almost evenly between light (interior) and dark (exterior), Hergé (and his team) poignantly extend this concern to the images themselves. Every image is occupied by frame-like constructs — doors, windows, carpeting, gates — through which the characters move, or aspire to move. Diagonals suggest depth, but also deliver avenues of blockage or passage, both for the characters and the reader’s eye as it crosses the rectangular grid of the page. A black cat discretely blocks the path out (panel 12), while an immobile car meet the characters. A disarray of tools are left at their disposal on the ground.
The cable from an unlit lamp — the sixth on their path through the page — snakes its way towards them, literally and metaphorically embodying their ambition, in that it provides Tintin with the idea of using its bulb as a distraction for the guards, to move them away from the twin, (finally) lit lamps that frame his and Haddock’s eventual route of escape. The page ends the way it started, with sound signaling an opening.
Hergé was fascinated by psychoanalysis and worked through these years with an Increasing awareness of the subconscious. In his comics, he attempts to articulate the knowable and the unknowable with equal clarity in a rich world of signs, of meaning. By presenting his subjective choices, he offers us an an avenue by which to make sense of things.
For more thoughts on Hergé by yours truly and cartoonist Thomas Thorhauge, go here.
Update by Noah: I’ve added the Dyspeptic Ouroboros label to make this part of our ongoing series on meta-criticism.
Utilitarian Review 6/19/10
Starting tomorrow, HU is going to host a roundtable on the marketing of art manga. We’re going to have a whole host of guest contributors…so click back through the week.
On HU
HU suffered a major outage and was down for 9 days. For a moment we thought we were going to lose about half our comments…but the folks at tcj, and especially blog admin Tom came through and managed to restore almost all the damage. More details here and here.
In less apocalyptic news; since the last link roundup, we completed our Asterios Polyp roundtable with posts by Caro, Robert Stanley Martin, me, and Matthias Wivel. Please note that all comments have not been restored to Caro and Robert’s posts; we’re hoping to fix that soon, but at the moment the threads may be a little disjointed.
Suat published a long two part discussion of The Times of Botchan. Part 1; Part 2.
Richard Cook reviewed Iron Man 2 the movie.
Vom Marlowe reviewed Connie Willis’ novel To Say Nothing of the Dog.
Suat discusses Walter Benjamin and comics criticism.
And finally, I have a cheesy country download available, and also a Scandinavian black metal download.
Utilitarians Everywhere
Both kinukitty and I participated in a roundtable about an academic collection of essays analyzing the Boys’ Love genre.
Kinukitty’s posts are here and here.
As it turns out, I was reminded of an observation by G.K. Chesterton. In a 1911 essay, he said (in his cheerful, racist turn-of-the-20-century British way) that he felt Japan had imitated many Western things — the worst Western things. “I feel as if I had looked in a mirror and seen a monkey,” he wrote. And, reading “Rewriting Gender and Sexuality in English-Language Yaoi Fan?ction,” I had a similar experience. I love yaoi. I love Weiss Kruez fanfiction. And, to be overly dramatic about it, this essay ground my longtime passion and obsession into dust and ashes. I looked in the mirror and saw a demographic slice, vaguely exotic, in a Dances with Manporn sort of way, and ready to be dispassionately observed.
My contributions are here and here.
This book really helped me come to terms with my past, my regrets, my desires. Speaking as a straight white cisgendered male, I occasionally regret my transgressive decision to drop out of grad school to explore the fluid, abject jouissance of the non-(i)voried and nontowered. But then I encounter a text like this, and in its quivering, jellylike prose I remember why, though riven by radical difference, still numerous numinous heterogenous communities speak with a single pleasurable speech-act when they utter: “academics fucking suck.”
Over at Comixology I discuss a classical Chinese Zen triptych featuring bodhisattva, crane, and monkey.
Kuan-yin’s calm here may be in contrast to these unenlightened viewers, who squat like monkeys or strut like cranes, curious but oblivious. Or, perhaps, the joke isn’t that the audience is unworthy of enlightenment; but rather that they are already enlightened. Because they are as undignified as the monkey or the crane, those who contemplate the picture have their own plain, contingent place within it, like cranes or monkeys who happen to be nearby when the bodhisattva comes.
At Splice today, I review new releases by Monica and Toni Braxton.
One of the more noticeable results of this transformation was that r&b semi-fused with rap, and the resulting homunculus took over the world. Less spectacularly, the change wreaked havoc with typical pop career arcs. In the normal course of things, you expect a pop act to release a few good albums, and then get progressively crappier until they finally attain a plateau of unlistenable awfulness and fade into oblivion. But after r&b as a genre exploded aesthetically, singers like Brandy and Mariah Carey found themselves doing their best work in their second decade rather than their first.
Also at Splice Today, I reviewed new albums by Christina Aguilera and black metal band Nachtmystium.
All of which leads me to conclude that, if given the choice, I’d rather hear Christina Aguilera perform black metal than listen to Blake Judd try his hand at pop R&B. Some musicians should stick to their roots; others can only get better the more thoroughly they betray themselves.
At Madeloud I have an interview with Norwegian black metal band 1349.
Many black metal musicians have been inspired by Satanism or alternately by traditional cultures or nationalism. Is that where you’re coming from at all? Or are there other beliefs and convictions you have which influence your music?
ARCHAON: For us this is about the art. But when that is said, it’s an artform coming from a background that had a great focus on such beliefs/convictions, and to a certain extent we are all believers of the individual being it’s own master – that’s where we would meet. Obviously, we are four individuals that would give you four different answers to this subject, but none of us are worshipers as such. And 1349 has never been a religious or a political band, and (most probably?) never will. Even though we’re all quite philosophical…I cannot see any of us going down that path, mate.
Also at Madeloud, I have reviews of two short albums by pop R&B group Allure, a review of 1349’s latest album Demonoir and a review of a new album by the dubstep duo Vex’d.