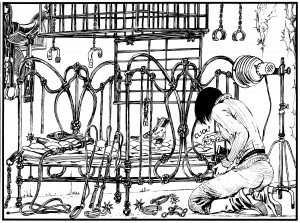
Carol Swain’s new graphic novel Gast (Fantagraphics, 2014)
After finishing Carol Swain’s Gast a few days ago, I found myself returning to Thierry Groensteen’s discussion of densité from Chapter 3 of Bande dessinée et narration (see pages 44 and 45 of the original French edition and page 44 of Comics and Narration, Ann Miller’s English translation). Gast, like Elisha Lim’s 100 Crushes (which I hope to write about soon), is a comic I’ve been enthusiastically recommending to friends. Swain tells the story of a young girl name Helen who, with the help of two dogs, a sheep, and a few birds, searches for clues about her neighbor Emrys and his sudden death.
I want to say very little about Helen and the small Welsh village where she and her family live. The mystery of Emrys’s life and death should reveal itself to the reader in the same slow, deliberate fashion that Helen comes to understand it. I’ll focus my attention instead on some of Swain’s page designs so as not to give away too much of the story. In Gast, the “density” of Swain’s compositions suggest the distance between Helen and Emyrs, a character who haunts the narrative. Like the protagonist of Chris Ware’s Jimmy Corrigan or Art Spiegelman’s Maus, Helen has the impossible task of piecing together the fragments left behind by a man reluctant to tell his story. Swain conveys Helen’s joy and confusion in a series of regular, nine-panel grids. These repetitions convey the density, I think, of Helen’s curiosity and of Emrys’s loneliness. At times, in fact, it is not clear where one begins and the other ends—an important point to consider, especially for the reader, who, like Helen, is left to decide why Emrys took his own life.
In order to apply Groensteen’s idea of densité to Gast I am thinking phenomenologically. Doing so opens up a number of theoretical possibilities, especially if the densité Groensteen describes can be read as synonymous, for example, with the density philosopher George Yancy examines in his recent book Look, a White! First, let me quote from Ann Miller’s English translation of Bande dessinée et narration before I consider density in relation to Yancy’s discussion of race: “A further consideration for the critical appreciation of page layout needs to be introduced,” Groensteen explains.
This is density, alluded to above. By this I mean the variability in the number of panels that make up the page. It is obvious that a page composed of five panels will appear less dense (as potential reading matter) than a page that has three times as many. (Groensteen 44)
What role does density serve, then, for both the artist and for the reader? Later in the chapter, Groensteen argues that, in Chris Ware’s comics, these dense and complex page designs have an expressive purpose: “Symmetry, in particular,” Groensteen argues, “is used by Ware to heighten the legibility of the binary oppositions that structure the spatio-temporal development of the story, such as interior/exterior, past/present, or day/night. But when two large images mirror each other on facing pages,” Groensteen adds, “this can also signify other oppositions or correspondences” (49-50). The “binary oppositions” Groensteen discusses here are also present in Gast: male/female, old/young, urban/rural, animal/human. The use of words and pictures to convey meaning in comics also implies the phenomenological density of consciousness itself: the sudden awareness of the self in relation to the other.
In Chapter 1 of Look, a White!, Yancy argues that what he describes as “the lived density of race” (17) demands new forms of expression. Although he is writing here about philosophy, I am interested in how we might apply his ideas to the comics we create, read, and study:
To communicate an experience that is difficult to express, the very medium itself may need to change. On this score, perhaps philosophers need to write poetry or make films. When it comes to a deeper, thicker philosophical engagement with issues of race, the medium has to change to something dynamically expressive, something that forces the reader/listener to feel what is being communicated, to empathize with greater ability, to imagine with greater fullness and power. (Yancy 30)
Notice that in his second sentence Yancy refers to poetry and film, two forms with close ties to comics (see, for example, Hillary Chute’s recent essay from Poetry Magazine). How might a page filled with words and pictures, for example, enable “the reader/listener to feel” with greater intensity? For Yancy, of course, this affective experience must accompany or inspire real change. Feeling something is one thing. Acting on a feeling of identification requires radical selflessness and love.
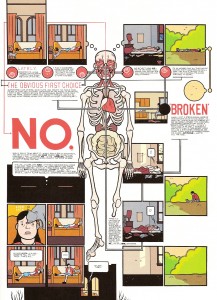
Page 127 of Gast
For Helen, the gradual shift from theory—her curiosity about Emrys’s life and death—to praxis takes shape on page 127, where she finds one of her neighbor’s books. In the first panel, we see a copy of Zane Grey’s Riders of the Purple Sage. The book is fragile. In the second panel, she tears the illustrated cover from its binding. “This book belongs to Emrys Bowen,” reads a note written on the back of the cover. In the fourth panel, she tucks that slip of paper beneath her arm, and holds the book in her hand in panel #5. She runs her fingers across the pages. Bits of paper fall like leaves.
Like Gatsby’s worn edition of Hopalong Cassidy in the final pages of Fitzgerald’s novel, Emrys’s copy of Riders of the Purple Sage reveals, perhaps, the dream image he cherished of himself. But, then again, no—as Helen tosses the book aside in the next panel, she implies that Emrys refused to play the role of the rugged cowboy. She conceals the torn cover in her bag.
Swain implies that, as readers, we would be wise to be suspicious of allusions. This sudden reference to another text cannot convey the full complexity of Emrys’s consciousness. As I read Gast, I thought of another writer who spent his career recording the silences of rural spaces. Most of the late John McGahern’s novels are set in Country Leitrim in northwest Ireland, not far from Yeats’s home of Sligo. In the introduction to his 1974 novel The Leavetaking, McGahern, who revised the novel in 1984, discusses the challenges of writing both self and other. “The Leavetaking was written as a love story,” McGahern explains,
its two parts deliberately different in style. It was an attempt to reflect the purity of feeling with which all the remembered “I” comes to us, the banal and the precious alike; and yet how that more than “I”—the beloved, the “otherest,” the most trusted moments of that life—stumbles continually away from us as poor reportage, and to see if these disparates could in any way be made true to one another. (McGahern 5)
Like Yancy, McGahern suggests other terms we might use to describe the density of experience expressed on page 127 of Gast: where do the “I” and “the ‘otherest’” meet?
As I study the last three panels on page 127, I find myself wishing I could retrieve Emrys’s copy of Riders of the Purple Sage. What if we missed something? What if the book contains the key to understanding Emrys? But the grid prevents me from turning back. I must follow Helen as she walks to Emrys’s house, just as I must follow McGahern’s narrator as he moves from rural Ireland to Dublin to London and back again (as I try to disentangle the real from the imagined in McGahern’s autobiographical fiction, most of which takes place in the same region of Ireland where my paternal grandmother, Mary Anne Bohan, was born in 1910).
Both McGahern and Swain tell their stories with clarity and compassion. Swain’s use of the grid, I think, is a reminder of the inevitable barriers between the subject and the object being observed. These barriers, like the borders that separate one panel from the next, suggest that densité is both an aesthetic choice and a phenomenological imperative: the storyteller and the reader must take into account what McGahern calls “the banal and the precious alike” in order to make less terrifying the space between the “I” and “the ‘otherest.'”
Can we read Groensteen’s densité, then, as a synonym for the density that Yancy describes? Can you think of other page designs that seek to express the phenomenology of the self? Do comics provide a means of eliminating the distance between the two?
References
Groensteen, Thierry. Bande dessinée et narration: Système de la bande dessinée 2. Paris: Presses Universitaires de France, 2011. Print.
Groensteen, Thierry. Comics and Narration. Trans. Ann Miller. Jackson: UP of Mississippi, 2013. Print.
McGahern, John. The Leavetaking. London: Faber and Faber, 1984. Print.
Swain, Carol. Gast. Seattle: Fantagraphics, 2014. Print.
Yancy, George. Look, a White! Philosophical Essays on Whiteness. Philadelphia: Temple University Press, 2012. Print.
This is a cross-post from my blog. Thanks to Qiana and Adrielle for inviting me! Thanks also to my dad’s cousin Oliver Gilhooley of Mohill, Co. Leitrim, for taking us to the John McGahern Library at Lough Rynn Castle in the summer of 2012. Oliver, a great storyteller himself, also gave us a suggested reading list of McGahern’s fiction.
The McGahern Library at Lough Rynn. Photo courtesy of Allison Felus.