Earlier this week, Nadim Damluji wrote a post discussing the painful Orientalism of Craig Thompson’s Habibi. Nadim sums up his argument as follows:
Wanatolia represents the poignant identity crisis at the heart of Habibi: it wants to be a fairytale and commentary on capitalism at the same time. The problem is that in sampling both genres so fluidly, Thompson breaks down the boundaries that keep the Oriental elements in the realm of make-believe. In other words, the way in which Wanatolia is portrayed as simultaneously savage and “modern” reinforces how readers conceive of the whole of the Middle East. Although Thompson is coming from a very different place, he is presenting the same logic here that stifles discourse in the United States on issues like the right to Palestinian statehood. If we are able to understand Arabs in a perpetual version of Arabian Nights, then we are able to deny them a seat at the table of “civilized discourse.”
Thompson self-consciously presents his Orientalism as a fairy-tale. Yet the fairy tale is so riveting, and his interest in the reality of the Middle East so tenuous, that he ends up perpetuating and validating the tropes he claims not to endorse. Here, as so often, what you say effectively determines what you believe rather than the other way around.
Thinking about this, I was reminded of one of Neil Gaiman’s most admired Sandman stories — Ramadan, written in the early 1990s and drawn by the great P. Craig Russell.
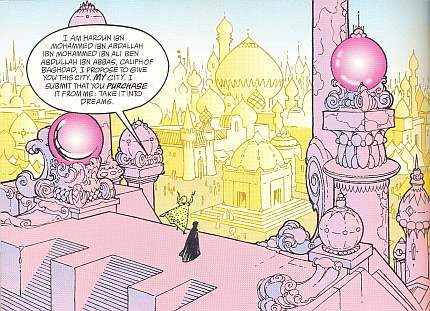
The beautiful opening page of Gaiman/Russell’s “Ramadan”.
I haven’t read Thompson’s Habibi, but from Nadim’s description, it seems that Gaiman and Russell are even more explicit in treating Orientalism as a trope or fantasy. The protagonist of “Ramadan” is Haroun al Raschid, the king of Baghdad, the most marvelous city in the world. Baghdad is, in fact, the mystical distillation of all the magical stories of the mysterious East. Gaiman’s prose evokes, with varying success the exotic/poetic flourishes of Western Oriental fantasy. At his best, he captures the opulent wonder of a well-told fairy-tale:
And there was also in that room the other egg of the phoenix. (For the phoenix when its time comes to die lays two eggs, one black, one white.
From the white egg hatches the phoenix-bird itself, when its time comes.
But what hatches from the black egg no one knows.)
At his worst, he sounds like a sweatily clueless slam poet: there’s just no excuse for dialogue like “I can smooth away the darkness in your soul between my thighs”.
But if Gaiman’s hold on his material wavers at times, Russell makes up for any lapses. Beneath his able pen, the Arabian Nights is transformed into sweeping art nouveauish landscapes, a ravishingly familiar foreign decadence.
As I said, this is all clearly marked as fantasy — both because there are flying carpets and Phoenixes and magical globes filled with demons, and because the whole point of the narrative is that it’s a story. As the story opens, Haroun al Raschid is dissatisfied with his city, because, despite all its marvels, it will not last forever. So he makes a bargain; he will sell Baghdad to Dream, and in return Dream agrees to preserve the city forever. The bargain made, the city vanishes into dream and story. And not just the Phoenix and the magic carpet disappear, but all the marvelous wealth and luxury and wisdom of the east, from the luxurious harems to the fantastic quests. Orientalism, as it is for Craig Thompson, becomes just a story which never was.
Gaiman and Russell, then, avoid Thompson’s error; they do not conflate reality and fantasy. Fantasy is in a bottle in the dream king’s realm, forever accessible, but never actual. The real Middle East, on the other hand, must deal with a grimmer truth; the last pages of the story show Iraq as it was in the early 90s — ravaged by sanctions, brutally impoverished, and generally a gigantic mess by any objective standards (though not, of course, by the standards of the Iraq of a decade later.) In this real Iraq of starvation and misery, the other Iraq is only a dream. As Gaiman says, speaking of an Iraqi child picking his way through the ruins, “he prays…prays to Allah (who made all things) that somewhere in the darkness of dreams, abides the other Baghdad (that can never die), and the other egg of the Phoenix.”
So that’s all good then. Except…whose is this dream of Orientalism, exactly? Well, it’s the Iraqi boys, as I said, and before his, it was Haroun al Raschid’s. But really, of course, it isn’t theirs at all. It’s Gaiman and Russell’s.
Orientalism does have some roots in Arabic stories; I’m not denying that. But this particular conception of the folklore of Arabia as a single, marvelous whole, containing all that is wonderful in the East, in contrast to a sordid, depressing reality — I don’t believe Gaiman and Russell when they say that that’s a thing in the mind of Iraqis. Habin al Raschid giving up his dream is a dream itself, and the dreamer doesn’t live anywhere near Baghdad.
“Ramadan,” then, is a tale about losing a fantastic land to fantasy — but it isn’t Habin al Raschid who loses it. Rather, it’s Gaiman and Russell and you and me, (presuming you and me are Western readers.) Gaiman and Russell are, like Thompson, nostalgic for Orientalism — they know it’s a dream, a vision in a bottle, but they just can’t bear to put the bottle down. Our fantasy Middle East is so much more glamorous than the real Middle East, even the people who live there must despair that our tropes are not their reality. Surely they want to be what we want them to be, democrats or kings, sensuous harem maidens or strong independent women. Thus the magical Arabia and the sordid, debased (but potentially modern!) Arabia live on together in the world of story, comforting Western tellers with the eternal beauty of loss. Our Orient is gone. Long live our Orient.
_______________
Nadim’s thoughts have inspired an impromptu roundtable on Orientalism. which can be read here as it develops.